Figure 3-9: King George Sound
King George Sound

Figure 3-9: King George Sound
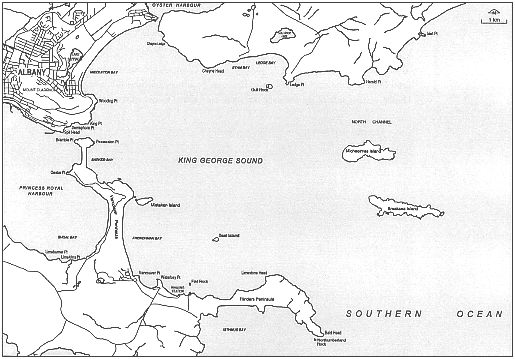
The sound covers an area of 110 km2 and forms a large bay protected from the prevailing south-westerly swells by Flinders Peninsula and Bald Head. The north-western and northern shores are formed by the mainland. The entrance to Oyster Harbour is on the north-western shore. The western shore is formed by Vancouver Peninsula, which separates the sound from Princess Royal Harbour.
The sound is open to the south-east but gains some protection from Michaelmas and Breaksea islands which lie north-east of Bald Head. Other islands in the sound are Seal Island, which lies north-west of Bald Head, and Mistaken Island, which lies just offshore from Vancouver Peninsula.
Water depths in the sound are 10-35 mrtres. The deepest part is a basin in Frenchman Bay which lies west of Seal Island. Temperatures vary more than the open sea because of the sound's shallowness compared to the sea.
| Location | Mean Temperatures (°C) | |
|---|---|---|
| Summer | Winter | |
| Open sea | 20.1 | 17.3 |
| King George Sound | 20.5 | 13.6 |
The shore of the sound consists of large granite outcrops which form headlands, cliffs and islands interspersed with extensive sandy beaches composed of granite sands. Flinders Peninsula consists of limestone and sand dunes lying on top of a granite substrate. The shore of the peninsula consists of high cliffs which plunge down into the sea. A series of beaches interrupted by granite headlands run north-west from the peninsula.
West of Waterbay Point is Whalers Beach, north of which is Vancouver, or Goode, Beach which extends to Mistaken Island. The shore swings north-west from Mistaken Island and consists of granite slopes with several small beaches in Whaling Cove. A sand beach forms the eastern side of the tombola connecting Point Possession to Quarantine Hill. The tombola is sensitive to erosion, though it hasn't been breached in European settlement days. There have been some close calls owing to storms.
Across from the entrance to Princess Royal Harbour the shore consists of steep and shallow granite slopes which rise towards Mount Adelaide. On the northern side of Mount Adelaide is Ellen Cove and the south-western end of Middleton Beach. The beach forms the north-western shore of the sound and extends as far as Emu Point and the entrance to Oyster Harbour. On the eastern side of the entrance the shore is composed of granite sand beaches and granite slopes which rise towards Mount Martin.
The waters of the sound are influenced by the Leeuwin Current which flows southward along the Western Australian coast from the tropical waters off Exmouth and North West Cape. The current consists of a band of warm, low salinity water which flows along the edge of the continental shelf. At Cape Leeuwin the current swings east onto the continental shelf and along the shore. It then follows the southern coast into the Great Australian Bight. The peak flow of the current is from May to August. The current moderates sea temperatures along the southern coast.
The sound has a variety of animals and plants that are common to the temperate zone, and even some tropical zone creatures (adults and juveniles) which are carried south by the current.
Marine algae is abundant on sub-tidal rocks (rocks which are always below the surface of the water). There are extensive seagrass beds in shallow protected water, such as at Frenchman Bay on the south-western shore.
Common species of fish found in the sound are salmon, herring, pilchard, leatherjacket, tuna, King George whiting, snapper and shark.